Linux: Useful Commands
Following from the previous Linux articles, we have covered most of the Linux basics. On here, we will look at some of the most useful commands that comes handy as you use Linux as your daily system.

| Command | Definition & Functions |
|---|---|
| man | Manual of any commands or programs. e.g man uname. |
| uname | List System Info, this includes OS versions, kernel. etc. |
| htop | Interactive real time processing monitoring application |
| grep | Searches text and string in a given file |
| find | Find files with a given name. e.g. find . -name Demo.txt |
| Ctrl+Alt+F1 | Linux is multiuser OS. This switches to user one (TTY) |
| tail -f | Displays the file in real time. Useful to monitor log files as it populates. |
| | | Lets you sends the output of one command to another. e.g cat syslog | grep "error" |
| lshw | List system hardware |
| lscpu | List CPU info |
| lspci | Displays information about each PCI bus on your system |
| df | Reports file system disk space usage |
| python -m http.server | Creates simple HTTP server, making the directory available in LAN |
| Chmod +x | Change modification to execute the app |
| ps | Let you take a look at current process in shell session. ID, TTY (TeleTYperwrtier), time and command name |
| Kill | When your program is unresponsive, use this command to terminate it. Kill firefox or Kill (ProcessID) |
| Ping | Let you check the internet connection on your device. Also used to request domain name or IP Address. |
| History | Shows all the commands written in the past |
| Which | output full path of shell command. e.g # /user/bin/python |
| shred | As name suggested, shred the file and corrupt it by overiding the file content repeatedly. Making it difficult to recover |
| whatis | Prints a single line description of any other commands |
| ifconfig | Displays network interface & IP Address |
| wget | world wide web get - retrieve content from the internet |
| iptable | Linux firewall filtering table |
| traceroute | Trace all the network hops and destinations |
| zip and unzip | Let you Zip and Unzip the file |
| passwd | Create or update passwords for existing users |
| Sudo | Command to escalate privileges in Linux |
Let's look at some examples of all the Commands listed above
Man
Used for displaying manual of any other commands or programs.
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[~]
└─$ man uname
Other similar commands to Manual are --help -help.
Uname
This command shows the type of OS, kernel, and the build dates
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[~]
└─$ uname -a
output:
┌──(jay㉿Kali)-[/home/kali]
└─$ uname -a
Linux Kali 5.18.0-kali5-amd64 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Debian 5.18.5-1kali6 (2022-07-07) x86_64 GNU/Linux
Useful for system admin and developers, if they require certain OS version to run specific program.
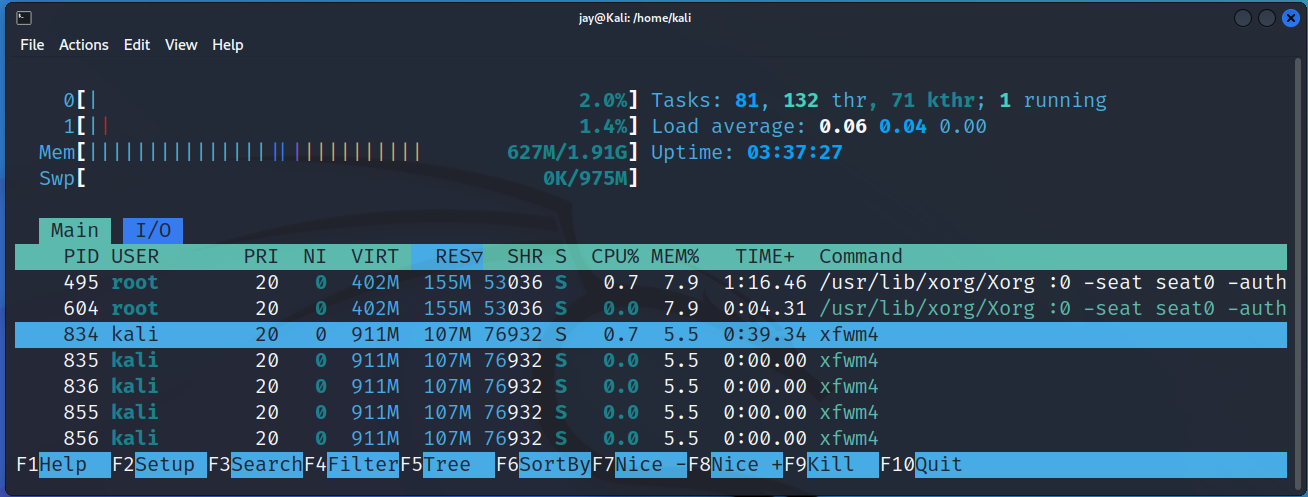
htop
Given an interactive system monitor process, and let you manager them.
┌──(jay㉿Kali)-[/home/kali]
└─$ htopoutput:
grep
Grep stands for (Global Regular Expression Print) This command used to search for text and strings in a given file.
Let's say you want to find a particular name in a file. You can simply write in the following syntax
grep <findme> <filename>
┌──(jay㉿Kali)-[/home/kali]
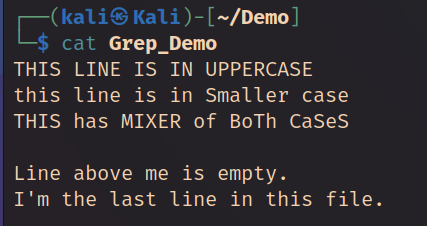
└─$ touch Grep_DemoWe have created a file with strings of text to showcase the example of `grep` search features.
Search for a string of text from multiple files
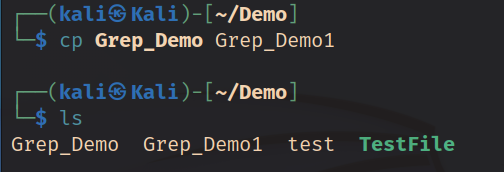
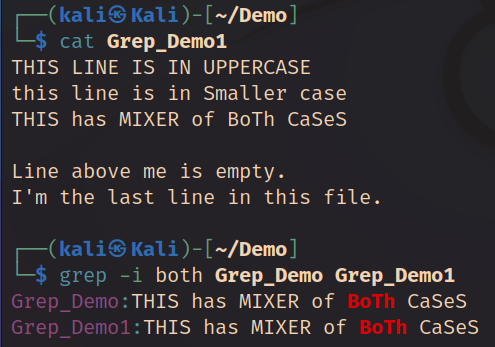
Screenshot above shows duplicating Grep_Demo file as Grep_Demo1, then search for text from both of the files, using -i flag to search for case insensitive texts.
find
Find command used to search and locate the list of files and directories based on specified arguments. we can find the files by permissions, users, groups, files types, date, size and other possible criteria.
Find files within user /home directory
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[~]
└─$ find /home -name Grep_Demo
find: ‘/home/jay’: Permission denied
/home/kali/Demo/Grep_DemoFind all the files based on user
This command to find all the files belong to user jay under /home directory
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[/home]
└─$ sudo find /home -user jay
/home/jay
/home/jay/.java
/home/jay/.java/.userPrefs
/home/jay/.java/.userPrefs/burp
/home/jay/.java/.userPrefs/burp/prefs.xml
/home/jay/.bash_logouttty (Teletype)
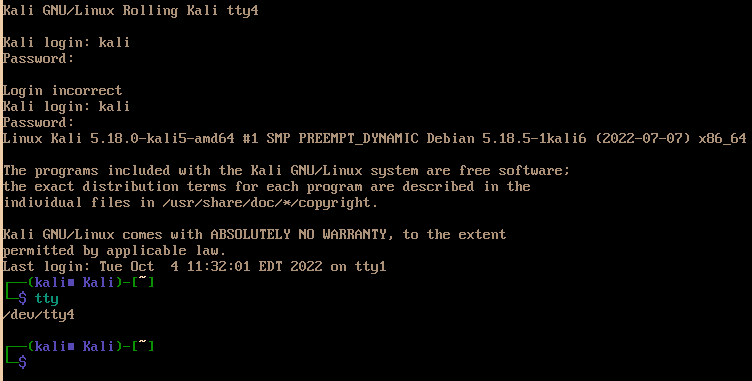
TTY is a Teletype virtual command. This can be used to diagnose the system or look up something as different terminal user.
Sample of using tty is to analyse CPU usage on our system using other virtual terminal. This also useful to check for any live log files using tail -f {filename} There are 1-6 terminals and you can switch between these by Ctrl +Alt + F1 to F7. Our current session is installed on F7.
The following screenshot shown we are using tty4 virtual terminal
tail
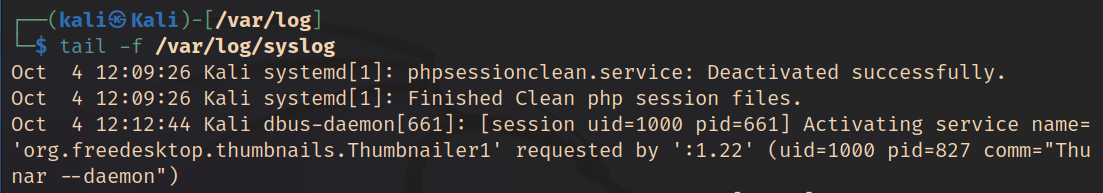
The tail command reads a file, and outputs the last section of the file (the tail)
The tail commands can be used to monitor data streams and open files that are currently being written new information. For an example system log files in real time. This can be done using -f switch, as shown below.
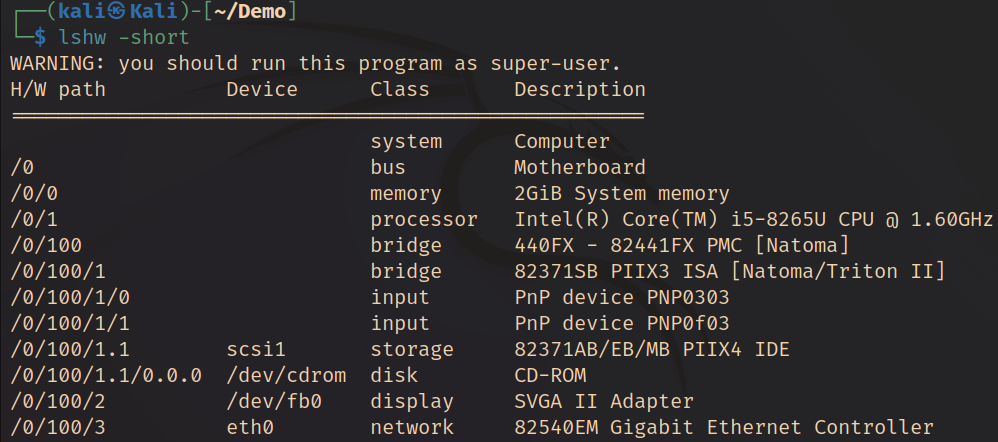
lshw
This command is a small tool to display a complete picture of hardware configuration.
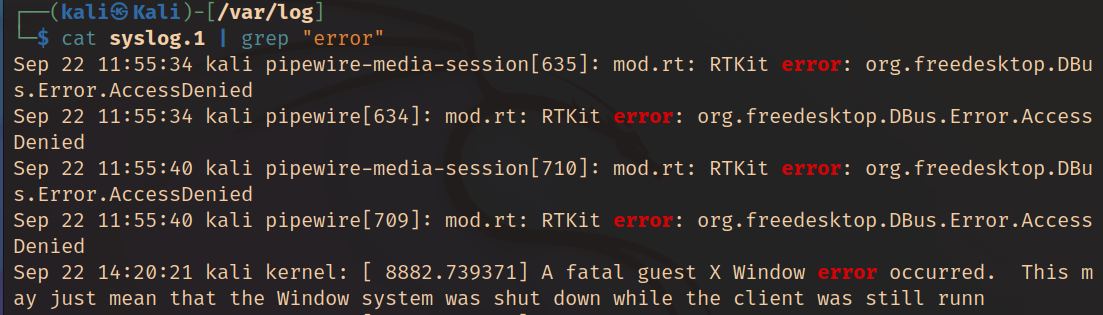
| (Shell Pipe command)
This | command
lets us out results from one command and use it as input to another command. For an example read the Syslog file, then search for text within it.
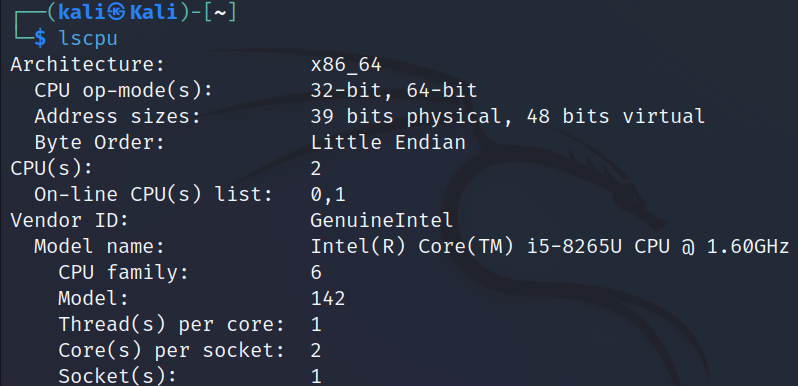
lscpu
A command-line utility “lscpu” in Linux is used to get CPU information of the system. This command fetches the CPU architecture information from the “sysfs” and /proc/cpuinfo files and displays it in a terminal.
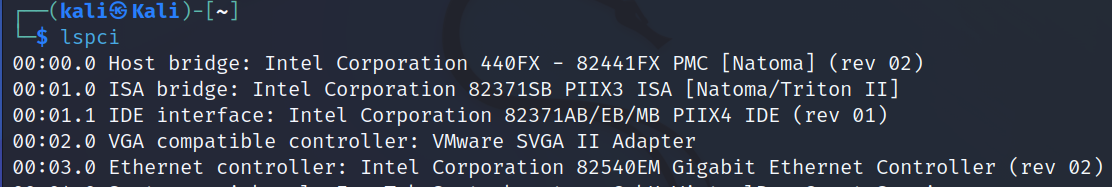
lspci
The lspci (list PCI) Linux command displays information about each PCI bus on your system. This includes information about the devices connected to the PCI subsystem.
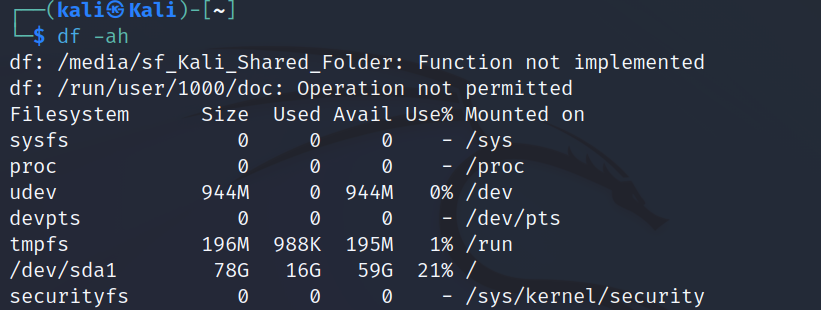
df
The df command displays the amount of disk space available on the filesystem with each file name's argument.
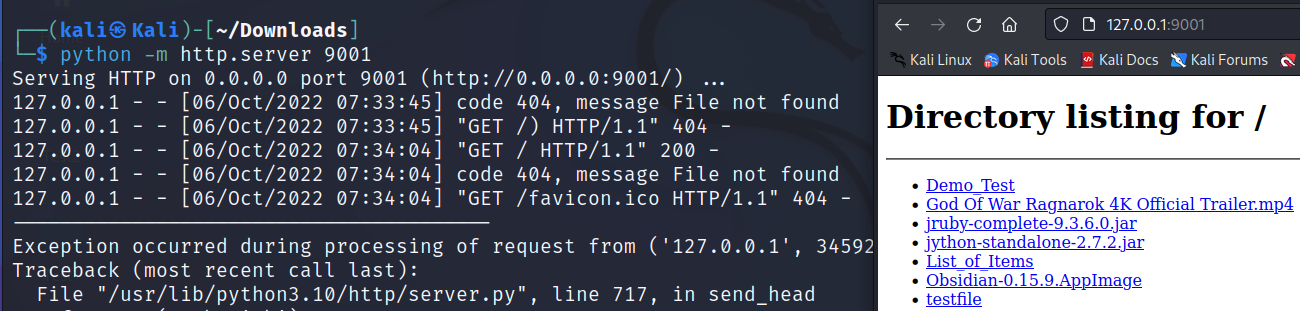
Simple HTTP Server
Easier way to share your directory within your local network. You can also specify the port number, so It does not conflict with used ports.
Python 2.x
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[~]
└─$ $ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000Python 3.x
┌──(kali㉿Kali)-[~]
└─$ $ python -m HTTPServer 8000"python --version"
Change modification to execute the file
The command chmod +x that is used to change file and folder permission. Find more details about chmod and chown commands in Linux: Beginners Guide 2
ps
This command is used to list the currently running processes and their (Process Identification Number) PIDs. A PID is automatically assigned to each process when it is created, a process is nothing but running instance of a program and each process has a unique PID on a Linux System.
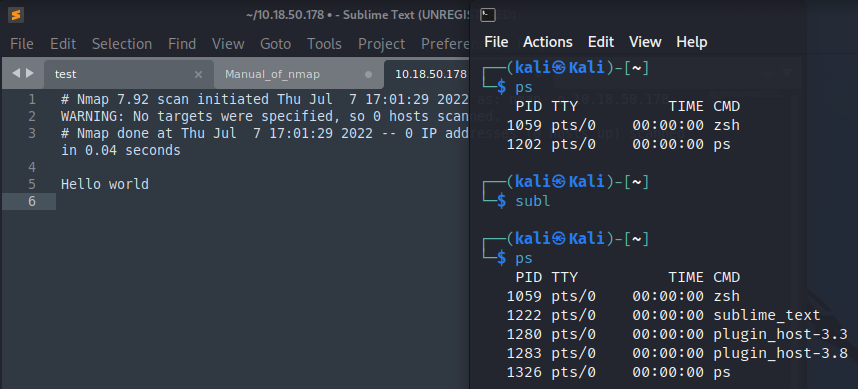
The above screenshot shows the sample of opening an Subl Text editor application and checking the running instance using ps command.
kill Command
Using the sample from previous ps command, we can terminate the application, using the PID number of the instance using. E.g Kill 1222. This will terminate the Sublime Text Editor.
ping
PING (Packet Internet Groper) command is used to check the network connectivity between host and server/host
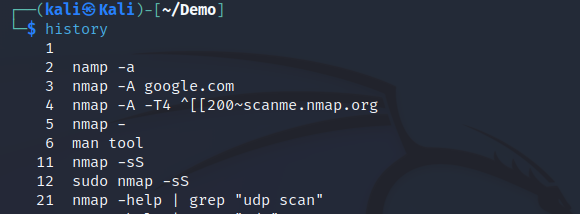
history
This command displays a list of commands used in the terminal sessions. This let users to reuse any listed commands without retyping it
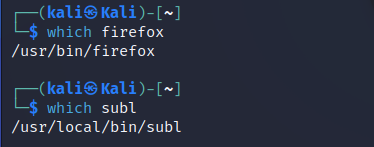
which
Which is used to locate the executable file associated with the given command by searching it in the path environment variable
shred
This command shred the data by overwrite the data in place several times and gives option to delete it, making it difficult to retrieve by third party software or hardware. Useful to delete sensitive data on your system.
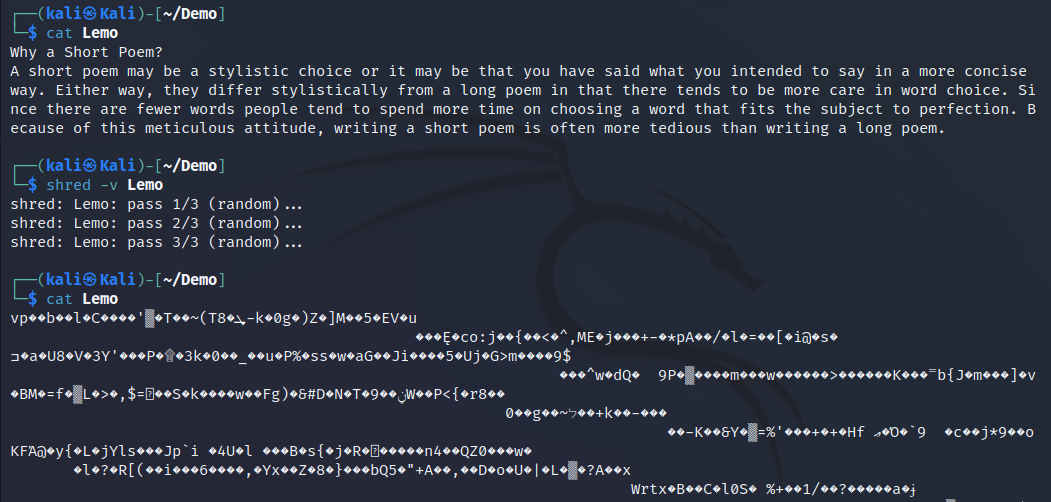
Another example of shredding the file using flags
- -v Stands for verbose, gives more detailed output
- -z Adds a zeros at final overwrite to hide shredding
- -u Removes files after shredding. We don't need to use rm command
- -n Overwrites files N times, instead of default (3 times)
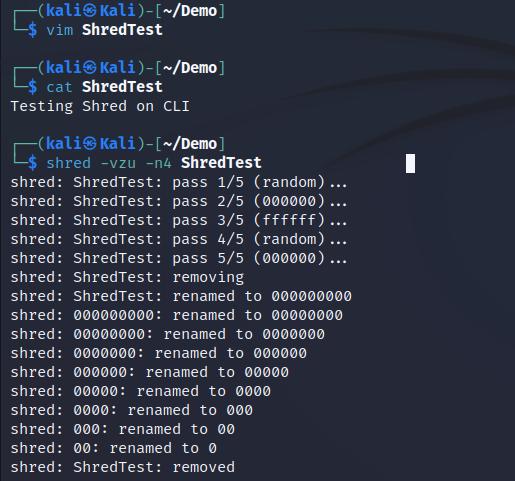
The following steps shows the detailed information about the screenshot above.
- As shown in the screenshot from line 1 -4, overwriting the file as we stated on our flag (-n4), then preparing to delete the file.
2. One additional overwrite the file with all zeros as we stated on flag (-z)
3. The filename is being overwritten to avoid being found after delectation.
4. Finally the file is removed
whatis
This command in Linux lets you display one line manual page descriptions.

We can also get multiple manual description by entering the commands with space.
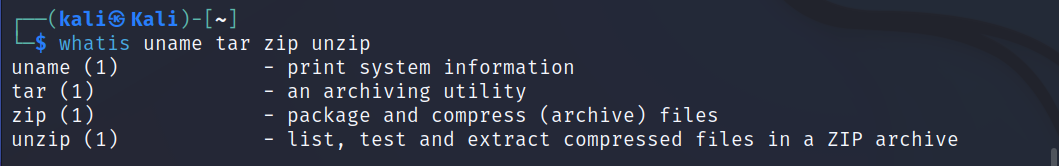
Using wildcards (*) Whatis command
Using the -w flag state the wild card search, then search for any commands that has "ls" in it. This will list all the commands that starts with ls as we can see below.

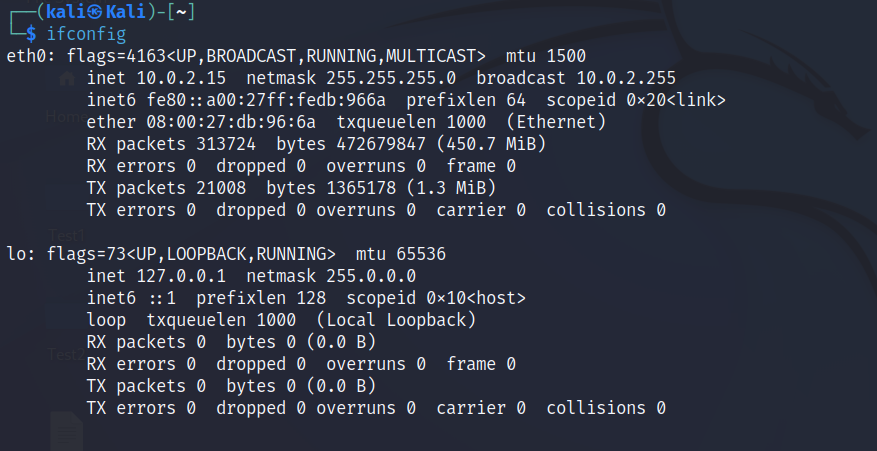
ifconfig
The ifconfig command is used for displaying current network configuration information, this includes ip address, netmask, or broadcast address to a network interface.
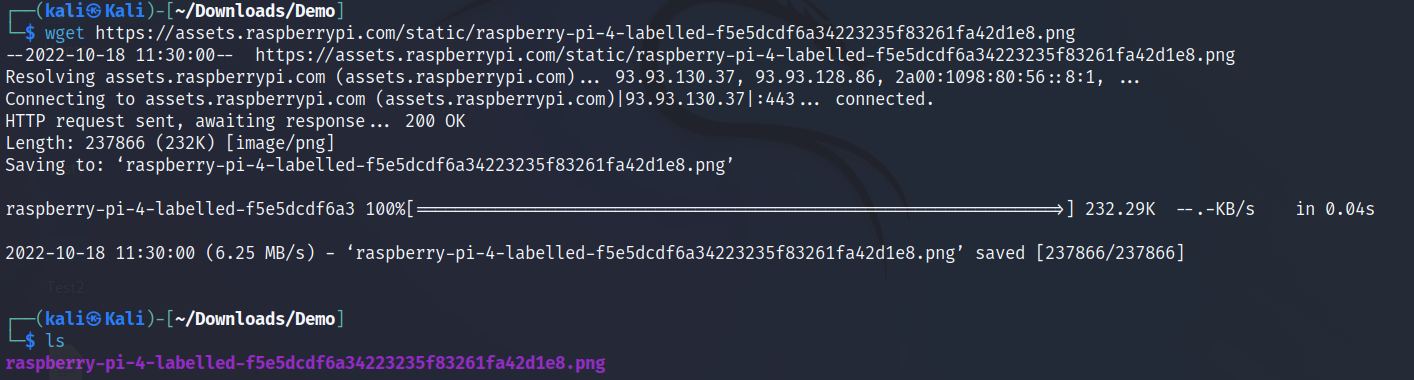
wget
This command let us download files from server, It supports HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP Protocols. wget is non-interactive, meaning that it can work in the background, while the user is not logged on.
The following screenshot shows the sample of downloading a Raspberry Pi 4 Diagram.
Firewall rules : iptable & ufw
Let's look at how this command function using Netfilter framework in Kernel.
Netfilter is a framework provided by Linux kernel, that let us manage the network by configuring it through IPtables and UFW (Uncompleted FireWall). Netfilter provides us with packet filtering, Network Address Translation (NAT), and Port Address Translation(PAT).
IPtables and UFW both are Linux system firewalls, the difference between them is UFW is built upon IPtables, and flexible tool that requires deeper understanding of TCP/IP. This passes rules directly to netfilter
In contrast, UFW is easy to use and less flexible, this passes the configurations form UFW to IPTables, which then sends those rules to netfilter. As name suggest uncomplicated firewall, this will be very user friendly for beginners.
traceroute
Traceroute is a monitoring command commonly used by network and system admin in their day to day operations.
Traceroute is monitoring command used by system admin to get find out the following
- Find out the complete path that a packet uses to reach its destination
- Discover the names and identify the routers and devices within the path
- Get the time duration it took to send and receive data to each devices on the path
Traceroute provide you a comprehensive info into the path our data will take to reach its destination, without sending any data through ICMP (Internet Communication Message Protocol)
All the packets send through the IP known as Time-To-Live (TTL) This means the maximum number of hops that a packet can travel across the internet before it gets discarded.
The purpose of TTL is to prevent the data packets from endlessly around the network, keeping the routers busy.
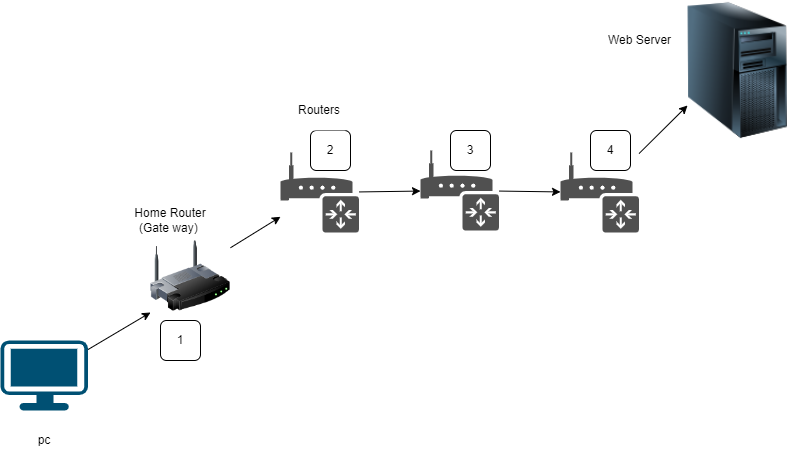
The diagram above illustrates how traceroute command communicate from pc to web server, through hops. Each number on the routers represents routers (hops) to communicate before it reaches to the destined host.
The following screenshot shows the example of traceroute
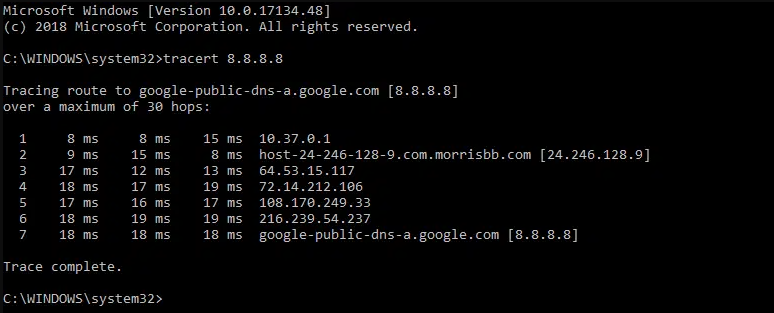
The first column shows us the number of hops router took to get to its destination, which shows 7 hops. The next three column shows the round trip time each data packet took for each data point and back our computer.
The first hop took 8 milliseconds as it is within the cooperate network, before reaching out to the internet. As the packet progress to server, the round trip time significantly increases.
When performing traceroute, it is important to keep an eye out for consistent round trip time, that gradually increase without any major gaps in time. This indicates everything is working fine without any delay between each routers (hops).
When there's a delay in response, we can look at which hops is causing the issue. In this case the 5th hop is causing the delay, therefore we know our local area network and google server is working fine.
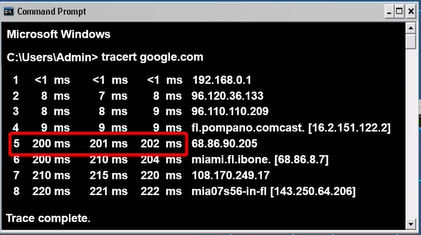
The Traceroute utility is a great tool to pinpoint any issues on network, and find any bottlenecks, that is slowing the traffic.
Sometimes It doesn't necessarily mean there's a problem, It could be the route is connecting to different continent.
Zip and Unzip Command
These two command let us compress multiple files into one file and vice verse.
If the zip command is not already installed on our system, we can run:
sudo apt-get install zipLikewise, for unzip command we can change zip to unzip on command above to install the unzip utility.
Once installed zip utility, we can compress the file as shown below
zip ZipFileName File1 File2 File3We can also extract to particular destination folder, as shown below
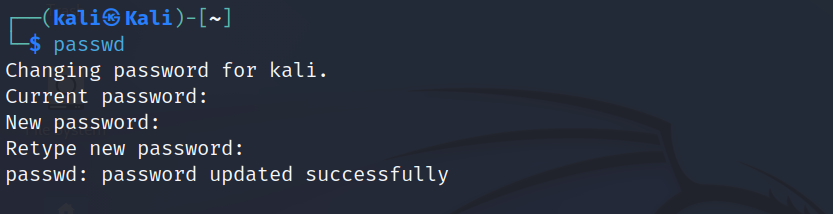
unzip ZipFileName -d destionation_folderpasswd
This command let us change or update our password. Typing passwd will walk us through the process as shown below
sudo
Sudo stands for SuperUser Do and it is used to access restricted files and tasks in Linux Distros. Also, it can be used to temporarily elevate user privileges allowing users to complete sensitive tasks without logging in as the root user.
If we have access to root user of the machine, we can pretty much do anything on the system.

Summary
These commands comes handy once you get used to it and try them out for yourself. Linux is a great open source OS that can run on any hardware without high-end processers and graphics.
Member discussion